Debugging AWS API Gateway Integration Errors: A Practical Checklist
AWS API Gateway is a powerful, fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale. It acts as the “front door” for applications to access data, business logic, or functionality from your backend services, whether they’re AWS Lambda functions, EC2 instances, or external HTTP endpoints.
However, despite its power, hitting an unexpected 5xx or 4xx error when trying to invoke your API can be a frustrating experience. API Gateway integration issues are a common roadblock, often stemming from misconfigurations between the API Gateway itself and its backend integration. Knowing how to debug AWS API Gateway effectively is a crucial skill for any cloud developer.
This article provides a practical checklist to help you troubleshoot REST API AWS integration errors systematically. By following these steps, you can quickly identify the root cause of common problems and get your APIs back on track.
Understanding API Gateway’s Role in the Request Flow
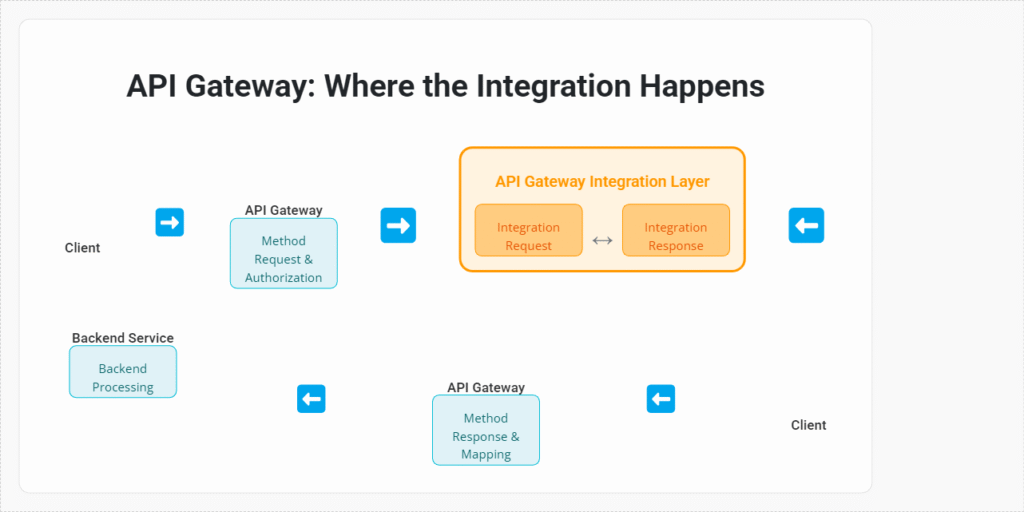
To effectively debug AWS API Gateway, it’s essential to visualize the request lifecycle. When a client makes a request to your API Gateway endpoint, it goes through several stages:
- Client Request: The client sends an HTTP request (e.g.,
GET /users). - API Gateway Method Execution: API Gateway receives the request and performs:
- Method Request: Validates request parameters, headers, and body against your API model.
- Authorization: Checks IAM permissions, Cognito authorizers, or Lambda authorizers.
- Mapping Templates (Request): Transforms the incoming client request into the format expected by your backend service.
- Integration Request: API Gateway forwards the transformed request to your backend. This is where most “integration errors” occur. The backend could be:
- Lambda Function: API Gateway invokes your Lambda.
- HTTP Endpoint: API Gateway acts as a proxy to an external URL.
- AWS Service: API Gateway integrates directly with other AWS services (e.g., DynamoDB, S3).
- VPC Link: For private integrations with resources in your VPC (e.g., EC2, ALB).
- Backend Processing: Your backend service processes the request and sends a response back.
- Integration Response: API Gateway receives the response from your backend.
- Mapping Templates (Response): Transforms the backend’s response into the format expected by the client.
- Method Response: API Gateway returns the final response to the client.
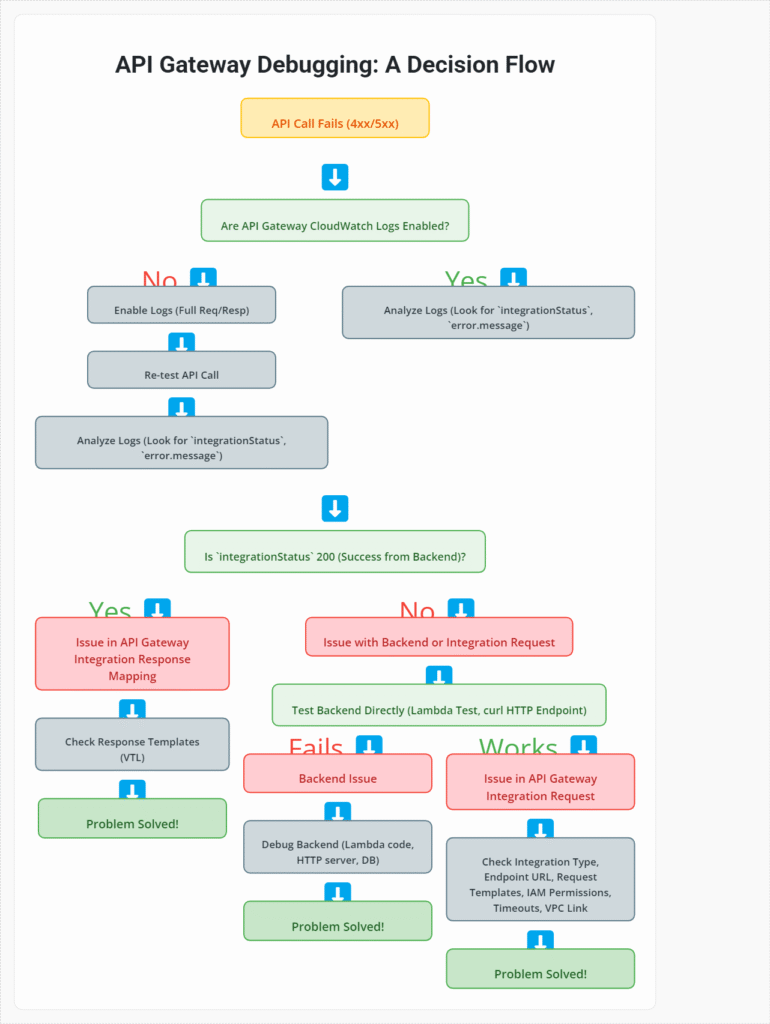
The Debugging Checklist: A Practical Approach to Troubleshoot REST API AWS
When faced with API Gateway integration issues, don’t just guess. Follow this systematic checklist to pinpoint the problem.
Step 1: Check API Gateway CloudWatch Logs (The First Line of Defense)
API Gateway’s detailed logging to Amazon CloudWatch is your most powerful debug AWS API Gateway tool.
- Enable Access Logging:
- Go to your API Gateway Console.
- Navigate to Stages, select your stage (e.g.,
prod,dev). - Go to the Logs/Tracing tab.
- Enable CloudWatch Logs and set the Log level to
INFOorERROR. For initial debugging,INFOis good, butERRORis sufficient for production. - Enable Full request and response data logging for detailed insights (disable in production due to cost/data sensitivity unless critical).
- Choose an IAM Role that allows API Gateway to write logs to CloudWatch.
- Analyze Logs in CloudWatch Logs Insights:
- Once logging is enabled and you’ve made some test calls, go to the CloudWatch Console.
- Select Logs Insights.
- Choose the log group for your API Gateway (e.g.,
/AWS/ApiGateway/YOUR_API_NAME). - Look for logs from your specific invocation. Key fields to examine:
status: HTTP status code returned to the client.integrationLatency: Time taken for the backend integration. High latency here points to a backend issue.integrationStatus: HTTP status code returned by the backend. This is crucial. A200here means the backend responded successfully, but the API Gateway’s integration or method response might be transforming it incorrectly or your backend sent an error code like 400 that API Gateway then propagated.responseLatency: Total time API Gateway took to respond.responseLength: Size of the response.error.message: Specific error messages from API Gateway (e.g., malformed integration response).x-amzn-errortype: Specific API Gateway error codes.
Common Log Messages to Look For:
Execution failed due to a timeout error: Backend took too long.Endpoint request timed out: Backend didn’t respond within the integration timeout.Invalid endpoint address: Issue with the integration endpoint URL.Unauthorized: Authorization problem (not necessarily an integration error, but good to check).Missing Authentication Token: Often a client-side issue, but can be a misconfiguration.Malformed integration response: Backend response format doesn’t match API Gateway’s expectations.
Step 2: Test the Backend Service Directly
Eliminate API Gateway from the equation to determine if the problem lies with your backend.
- For Lambda:
- Go to the Lambda Console.
- Invoke the Lambda function directly using the “Test” button. Provide a sample payload that mimics the API Gateway request.
- Check the Lambda logs (in CloudWatch) for errors, exceptions, or incorrect logic.
- Ensure the Lambda function has sufficient memory and timeout settings.
- For HTTP Endpoints:
- Use
curl, Postman, Insomnia, or a browser to hit your HTTP endpoint directly, bypassing API Gateway. - Verify the endpoint is accessible, responds correctly, and returns the expected data format.
- Use
- For AWS Services (e.g., DynamoDB, SQS):
- Use the AWS CLI or SDK to perform the exact action the API Gateway integration is trying to perform.
- Check if the service responds as expected and that the credentials used (via the Lambda execution role or API Gateway’s service role) are valid.
Step 3: Verify Integration Type and Endpoint URL
A fundamental misconfiguration.
- Integration Type:
- Is it
Lambda Function,HTTP,AWS Service, orVPC Link? Ensure it matches your backend.
- Is it
- Endpoint URL / Lambda Function ARN:
- HTTP Integration: Double-check the URL for typos, missing
http://orhttps://, or incorrect paths. - Lambda Integration: Verify the Lambda function ARN is correct.
- VPC Link: Ensure the correct VPC Link is selected and it points to the right ALB/NLB.
- HTTP Integration: Double-check the URL for typos, missing
Step 4: Examine Integration Request and Response Mapping Templates
This is a common source of subtle API Gateway integration issues. API Gateway uses Velocity Template Language (VTL) to transform data.
- Request Mappings:
- Does your backend expect specific headers, query parameters, or a particular JSON structure?
- Is API Gateway correctly mapping the client’s request into that format?
- Common issues:
- Missing or incorrect headers (e.g.,
Content-Type). - Incorrect JSON paths (e.g.,
$.bodyvs.$.input). - Lambda Proxy vs. Non-Proxy Integration:
- Lambda Proxy Integration: API Gateway sends the raw event to Lambda. Your Lambda code needs to parse the event (e.g.,
event.body,event.headers). No request mapping is needed in API Gateway. - Non-Proxy Integration: You must explicitly map request parameters/body in API Gateway. If you’re seeing empty or malformed
eventobjects in Lambda, you might be using non-proxy with a Lambda expecting proxy behavior, or vice-versa.
- Lambda Proxy Integration: API Gateway sends the raw event to Lambda. Your Lambda code needs to parse the event (e.g.,
- Missing or incorrect headers (e.g.,
- Response Mappings:
- Does your API Gateway expect a specific response format from the backend before sending it to the client?
- Are you mapping backend error responses (e.g., a
500from Lambda) to the correct API Gateway method responses? - Common issues:
- Backend returns plain text, but API Gateway expects JSON (or vice-versa).
- Error handling: If your backend returns a custom error structure, you might need to map it to a
4xxor5xxmethod response in API Gateway.
How to Check:
- In the API Gateway Console, go to your Method.
- Click on Integration Request and Integration Response.
- Review the Mapping Templates. Use the “Test” feature within API Gateway (under the Method Execution page) to send a sample request and see the transformed request and response.
Step 5: Validate IAM Permissions (Execution Role)
The Lambda execution role or the API Gateway service role might lack necessary permissions.
- Lambda Integration:
- Does the Lambda function’s execution role have permissions to access downstream services (e.g.,
dynamodb:PutItem,s3:GetObject)? Check the Lambda’s CloudWatch logs forAccessDeniederrors. - Does the API Gateway service role (if using a direct AWS Service integration) have permissions to call the target AWS service?
- Does the Lambda function’s execution role have permissions to access downstream services (e.g.,
- VPC Link Integration:
- The API Gateway execution role needs permissions to use the VPC Link.
- The backend (e.g., ALB/NLB) needs to allow traffic from the security groups associated with the VPC Link.
Step 6: Review Timeout Settings
Timeouts can cause 504 errors or Execution failed due to a timeout error in logs.
- API Gateway Integration Timeout: Default is 29 seconds. If your backend takes longer than this, API Gateway will time out.
- Adjust in Integration Request settings if your backend legitimately needs more time (up to 29 seconds).
- Lambda Function Timeout: Default is typically 3 seconds.
- Ensure your Lambda function has a timeout greater than its expected execution time.
- API Gateway’s timeout should generally be less than or equal to the Lambda timeout.
Step 7: Check VPC Link and Security Group/Network ACLs (For Private Integrations)
If your API Gateway integrates with a private resource in a VPC via a VPC Link:
- VPC Link Status: Is the VPC Link
AVAILABLE? If it’sPENDINGorFAILED, it’s not ready. - Target Group Health: Is the target group (for ALB/NLB) associated with the VPC Link healthy and has registered targets?
- Security Groups:
- The security group attached to your ALB/NLB should allow inbound traffic from the security groups used by the VPC Link.
- The security group attached to your backend instances/containers should allow inbound traffic from the ALB/NLB’s security group.
- The security group attached to your Lambda ENIs (if Lambda is in VPC) must allow outbound traffic to your private resources.
- Network ACLs: Ensure Network ACLs on your subnets are not blocking traffic.
Step 8: Examine Caching (If Enabled)
If API Gateway caching is enabled, you might be serving stale data or caching an error response.
- Clear Cache: Temporarily disable caching or clear the stage cache for debugging.
- Cache Keys: Ensure your cache keys are correctly configured and not leading to unintended caching behavior.
Step 9: Use the API Gateway Test Utility
The “Test” feature in the API Gateway console (under the Method Execution section) is invaluable.
- It allows you to simulate requests to your API Gateway method.
- It shows you the transformed request sent to the integration backend, the raw response from the backend, and the final response returned to the client. This helps you identify issues in mapping templates.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Debugging AWS API Gateway
API Gateway integration issues are a common, but solvable, challenge in serverless development. By systematically applying this practical checklist, you can effectively debug AWS API Gateway configurations and quickly identify the root cause of errors.
Remember to leverage CloudWatch Logs as your primary diagnostic tool, isolate the problem by testing your backend directly, and meticulously review your integration settings, mapping templates, and IAM permissions. Mastering the art of troubleshoot REST API AWS is crucial for building robust, reliable, and production-ready serverless applications.



