Optimizing AWS EC2 Spot Instance Usage for Intermittent Workloads: A Practical Guide
In the world of cloud computing, cost efficiency is as crucial as performance and scalability. For many organizations, Amazon EC2 instances represent a significant portion of their AWS bill. While On-Demand instances offer immediate availability and Reserved Instances provide predictable discounts for steady-state workloads, neither is ideal for tasks that are flexible, fault-tolerant, and don’t require continuous compute capacity. This is where AWS EC2 Spot Instances shine, offering a powerful avenue for AWS EC2 Spot Instance cost savings.
Spot Instances allow you to bid on unused EC2 capacity, often at discounts of up to 90% compared to On-Demand prices. The catch? AWS can reclaim these instances with a two-minute warning if the capacity is needed elsewhere. This makes them perfectly suited for running intermittent jobs on AWS Spot and highly effective for EC2 Spot Instance for batch processing and other flexible workloads.
This practical guide will delve into how to effectively leverage EC2 Spot Instances, providing strategies and best practices to optimize their usage for intermittent and fault-tolerant tasks, ensuring you maximize your savings without compromising your operations.
Understanding EC2 Spot Instances: The Fundamentals
Before optimizing, it’s vital to grasp the core mechanics of Spot Instances:
- Pricing Model: Spot Instance prices fluctuate based on supply and demand for a given instance type in a specific Availability Zone (AZ). You pay the Spot price that’s in effect for the time your instances are running.
- Interruptibility: This is the key difference. If AWS needs the capacity back (due to increased On-Demand demand or internal needs), your Spot Instance will receive a two-minute interruption notice before it’s terminated or stopped.
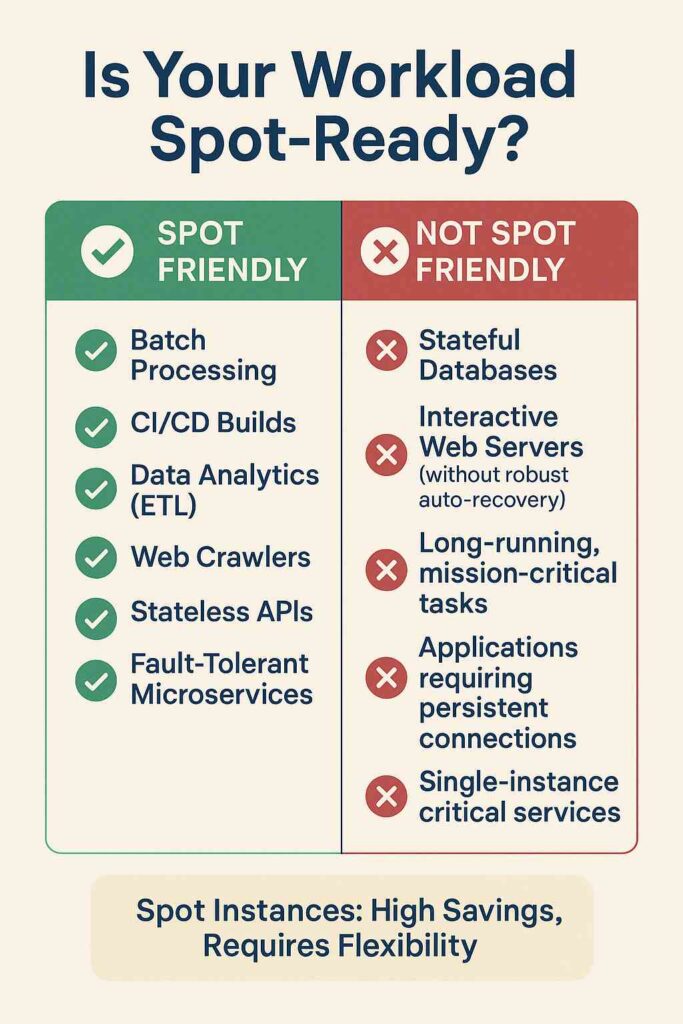
- Workload Suitability: Due to their interruptible nature, Spot Instances are best for stateless, fault-tolerant, or flexible workloads that can gracefully handle interruptions.
Ideal Use Cases for Spot Instances:
- Batch Processing: Processing large datasets, image rendering, video encoding, scientific simulations.
- CI/CD Pipelines: Running tests, builds, and deployments that can restart or resume.
- Data Analytics: ETL jobs, big data processing (e.g., Spark, Hadoop clusters).
- Web Crawling/Scraping: Tasks that can be easily distributed and restarted.
- Containerized Workloads: Microservices that are designed to be stateless and resilient (e.g., on ECS, EKS with Spot nodes).
Practical Strategies for Running Intermittent Jobs on AWS Spot
Leveraging Spot Instances effectively requires a strategic approach to your application architecture and deployment.
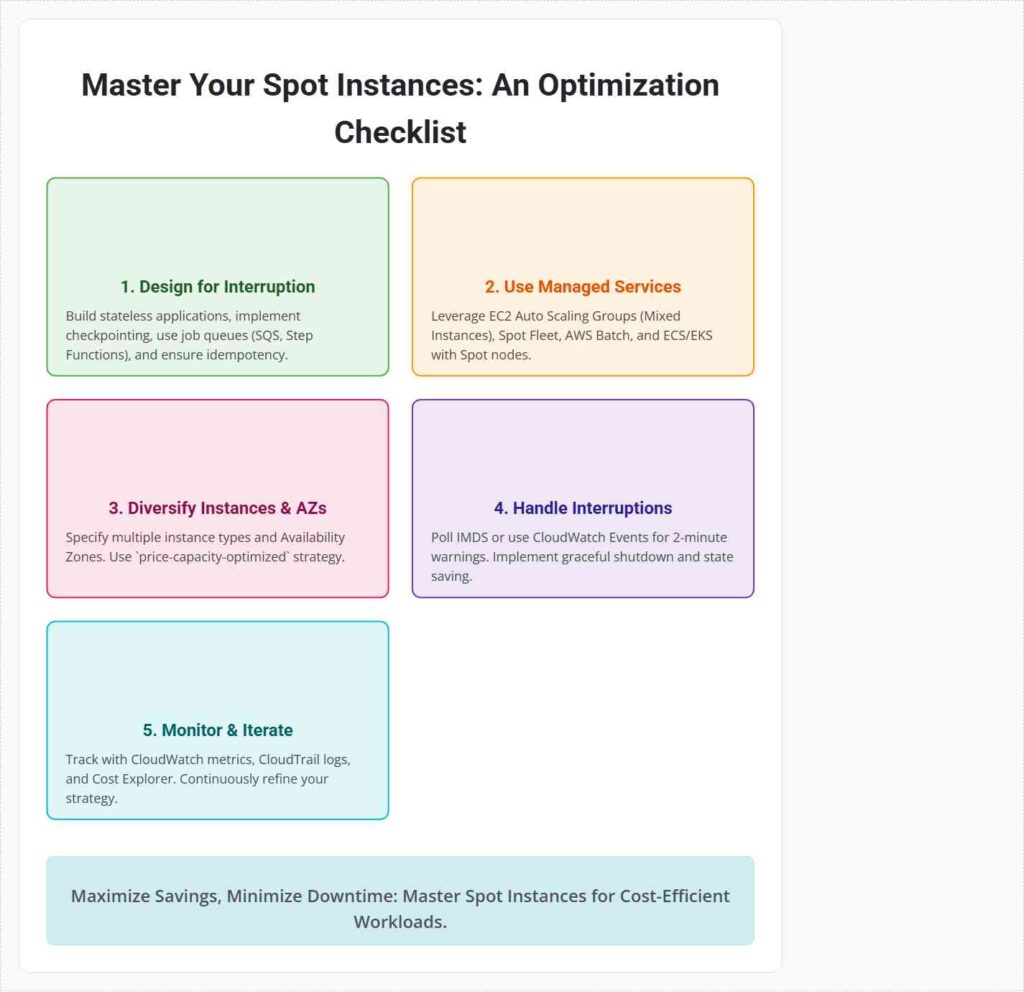
1. Decouple and Design for Interruption Tolerance
This is the golden rule for EC2 Spot Instance for batch processing and any other intermittent workload.
- Stateless Applications: Ensure your application instances don’t store critical session data or unique state on local storage. Use external storage like Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB, or Amazon RDS for persistent data.
- Checkpointing/Resumption: For long-running batch jobs, implement checkpointing. Periodically save the job’s progress to persistent storage so it can resume from the last checkpoint if interrupted.
- Job Queues: Use message queues like Amazon SQS or AWS Step Functions to manage job processing. Workers (on Spot Instances) pull tasks from the queue. If a worker is interrupted, the task returns to the queue for another worker to pick up.
- Idempotency: Design operations to be idempotent, meaning they can be safely retried multiple times without causing unintended side effects (e.g., creating duplicate records).
2. Utilize AWS Services Designed for Spot
AWS offers services that simplify the orchestration and management of Spot Instances.
- EC2 Auto Scaling Groups with Spot:
- Configure an Auto Scaling Group (ASG) to launch Spot Instances.
- Use a mixed instances policy to combine On-Demand and Spot Instances within the same ASG. This ensures a baseline of availability with On-Demand while maximizing Spot savings.
- Specify multiple instance types and Availability Zones (AZs) in your ASG. This increases your chances of getting Spot capacity and reduces the likelihood of interruption.
- EC2 Fleet & Spot Fleet:
- These services allow you to launch a “fleet” of Spot Instances (and optionally On-Demand) across various instance types and AZs to meet a target capacity.
- They automatically provision and maintain your desired capacity, replacing interrupted instances with new ones from available pools.
- Ideal for large-scale, distributed workloads.
- AWS Batch:
- A fully managed batch computing service that can provision compute environments (including Spot Instances) for your batch jobs.
- AWS Batch handles queueing, scheduling, and execution of jobs, automatically spinning up and down Spot Instances as needed. It’s an excellent choice for EC2 Spot Instance for batch processing.
- Amazon ECS/EKS with Spot:
- When running containerized applications, you can configure your ECS clusters (using EC2 launch type) or EKS node groups to use Spot Instances.
- ECS supports Spot-only capacity providers, and EKS leverages Karpenter or the Cluster Autoscaler with Spot Instances to manage pod scheduling on interruptible nodes.
- This is a powerful combination for running intermittent jobs on AWS Spot within a containerized environment.
3. Optimize Instance Selection and Diversity
To maximize AWS EC2 Spot Instance cost savings and minimize interruptions, diversify your instance strategy.
- Multiple Instance Types: Don’t stick to just one instance type. List several instance types that meet your application’s resource requirements (e.g.,
m5.large,m5a.large,m5n.large,c5.large,c5a.large). This gives App Runner more options if one type becomes unavailable. - Multiple Availability Zones: Distribute your Spot Instances across several Availability Zones within a region. Spot prices and availability vary by AZ, so diversifying reduces interruption risk.
- Price Capacity Optimized Allocation Strategy: When using Spot Fleets or ASGs with mixed instances, use the
price-capacity-optimizedallocation strategy. This strategy automatically selects the optimal Spot pools based on historical interruption rates and current Spot prices, balancing cost savings with interruption likelihood.
4. Handle Spot Instance Interruptions Gracefully
While you aim to minimize interruptions, you must be prepared for them.
- Spot Instance Interruption Notice: AWS sends a two-minute warning before an instance is terminated or stopped. Your application should be designed to receive and act on this notice.
- Metadata Service: Poll the EC2 Instance Metadata Service (IMDS) endpoint (
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/spot/instance-action) every few seconds. - CloudWatch Events/EventBridge: Create a CloudWatch Event Rule that captures EC2 Spot Instance interruption warnings (event type
EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning). This can trigger a Lambda function to drain connections, save state, or perform cleanup.
- Metadata Service: Poll the EC2 Instance Metadata Service (IMDS) endpoint (
- Graceful Shutdown: Upon receiving an interruption notice, your application should:
- Stop accepting new tasks.
- Finish current tasks if possible within the two-minute window.
- Save any in-progress work to persistent storage (S3, DynamoDB).
- Deregister from load balancers or service discovery.
- Exit cleanly.
5. Monitor and Iterate
Continuous monitoring helps you refine your Spot Instance strategy for maximum AWS EC2 Spot Instance cost savings.
- CloudWatch Metrics: Monitor key metrics like:
SpotInstanceRequestFulfilledAndCapacityConsumed(for fulfillment success).Interruption Rate(if available via AWS Console or metrics for your specific instance types/AZs).- Application-specific metrics (job completion rates, errors).
- CloudTrail Logs: Review CloudTrail logs for
TerminateInstancesorStopInstancescalls originating from Spot interruptions. - Cost Explorer: Use AWS Cost Explorer to track your Spot Instance spending and compare it against On-Demand costs to quantify your savings.
- Experiment: Start with a portion of your workload on Spot, monitor performance, and gradually increase Spot usage as you gain confidence.
Conclusion: Unlocking Significant AWS EC2 Spot Instance Cost Savings
Optimizing AWS EC2 Spot Instance usage for intermittent workloads is one of the most effective strategies for realizing substantial AWS EC2 Spot Instance cost savings. While they require a different architectural mindset compared to always-on instances, the benefits in terms of cost reduction are immense.
By designing your applications to be interruption-tolerant, leveraging AWS services that simplify Spot management, diversifying your instance choices, and implementing robust interruption handling, you can confidently utilize EC2 Spot Instance for batch processing and other flexible tasks. Embrace Spot Instances as a core component of your cloud architecture to run intermittent jobs on AWS Spot efficiently and achieve remarkable cost optimization in your AWS environment.



